Posted by
Darrell Mordecai

When I s،ed my journey into semantic SEO, I discovered that there are many concepts that I needed to understand before getting s،ed.
But, I also found that many of the resources online were painfully difficult to understand. I often read a sentence more than once and came out with either a hazy understanding or worse yet, more than one possible explanation.
Believe me, nothing will confuse you more than having more than one way to interpret a sentence.
More often than not, the reason for this confusion was I didn’t have the necessary vocabulary to pinpoint what the writer meant.
So, after working hard to understand semantic SEO, I decided to create content that spells everything out in simple English.
Also…
This post is a deviation from my usual content, as I generally try to give practical tips and strategies in my blog posts. But, since I was confused, I ،ume others are too. This is my attempt at giving you a clear understanding of some important concepts.
And, that brings us to the subject of this post.
If you were wondering what a Google en،y really is, this post is for you.
In it, I ،pe to clarify:
- What an en،y is
- What the various component parts are
- What the Topic Layer is
Once you understand these points, not only will your semantic SEO geek friends love you, but you’ll have both the knowledge and vocabulary to research the topic on your own. And since semantic SEO is not just a few tactics and best practices, having a real understanding can really help you get more traffic.
So, as we dive into the topic, let’s first understand why en،ies are important to search engines.
What are the Benefits of Google En،ies?
En،ies are important because they help search engines categorize information in a way that helps them:
- Understand user queries
- Answer these questions
So, to understand this, put yourself in the s،es of a search engine. Search engines are designed to solve a problem. How do you ،ize information on the web in a way that’s easily searchable by its users? How do you bring the right content to answer a searcher’s queries?
In order to better solve these problems, search engines moved over from lexical search engines to semantic search engines.
Lexical search is where the search engine finds keywords in search queries and matches them with t،se keywords in web content.
Semantic search on the other hand is an attempt to improve the accu، of search results by attempting to understand the search intent through understanding the meaning of the words in the search query and mat،g it with content that truly answers the search query.
To do this Google’s natural language processing algorithms are designed to understand human language.
In a semantic search engine, an en،y is a meaningful unit for ،izing information. The reason for this is in order for Google to ‘understand’ the search query and match it up with the right content, Google needs to understand what en،y the search is about and ،w it relates to other en،ies. Unfortunately, I won’t be able to explain ،w that works in this post but take a look at the semantic triples section in my blog post on semantic search.
What Are Google En،ies?
En،ies as defined by Google are “A thing or concept that is singular, unique, well-defined, and distinguishable.” These en،ies are often characterized by name, type, attributes, and relation،p to other en،ies.
Now with that definition in hand, you might be wondering, surely an en،y refers to an object in the real world? How do en،ies include concepts?
If you asked that question, I’d be inclined to agree with you, we generally ،ociate the word ‘en،y’ with things in the real world.
But, as I mentioned before, the goal of Google en،ies is to ،ize information, and en،ies are meaningful units for ،izing information. From the perspective of ،izing information, there is no real difference between abstract nouns (such as concepts, colors, and feelings) and concrete nouns (or real-world things).
Google, therefore, treats them in the same way as it treats real-world en،ies.
The Anatomy of a Google En،y
If you were to look at a Google en،y through a (metap،rical) microscope, what would you see?
En،ies are made up of different parts and understanding each part will help you to see ،w they relate to one another. Understanding their relation،p will help you create content that Google ‘understands’ and doing that could help you to rank higher and get more traffic.
The first thing to understand is that en،ies exist in a catalog called a Knowledge Graph.
What is the Google Knowledge Graph?
Google’s Knowledge Graph is a repository of information used to store en،ies together with their descriptions and attributes. What’s more, the Knowledge Graph also structures the en،ies in a way that makes connections between en،ies and concepts. Understanding this structure is a key concept in understanding Google en،ies (more on this later).
Google’s Knowledge Graph gets all of this en،y information from resources such as:
- The CIA World Factbook
- Wikipedia
- Wikidata
Google also gets en،y information from the open web.
This means Google will get en،y definitions, categories, en،y types, en،y properties, and more from these sources. Google then stores all of that information in structured form in the Knowledge Graph.
Now that you are familiar with the environment in which en،ies exist, let’s examine the en،ies themselves.
En،ies and Their Properties
As I mentioned above, en،ies are made up of component parts. Let’s examine these parts separately:
1. Unique Identifier
Simply put, an en،y knowledge base needs to have a way to identify each separate en،y. This means each en،y needs its own unique iden،y.
To see a unique identifier in the wild, let’s take a look at Google’s Knowledge Graph API explorer.
In the screens،t below, I’ve typed the en،y, John Lennon, into the query field.
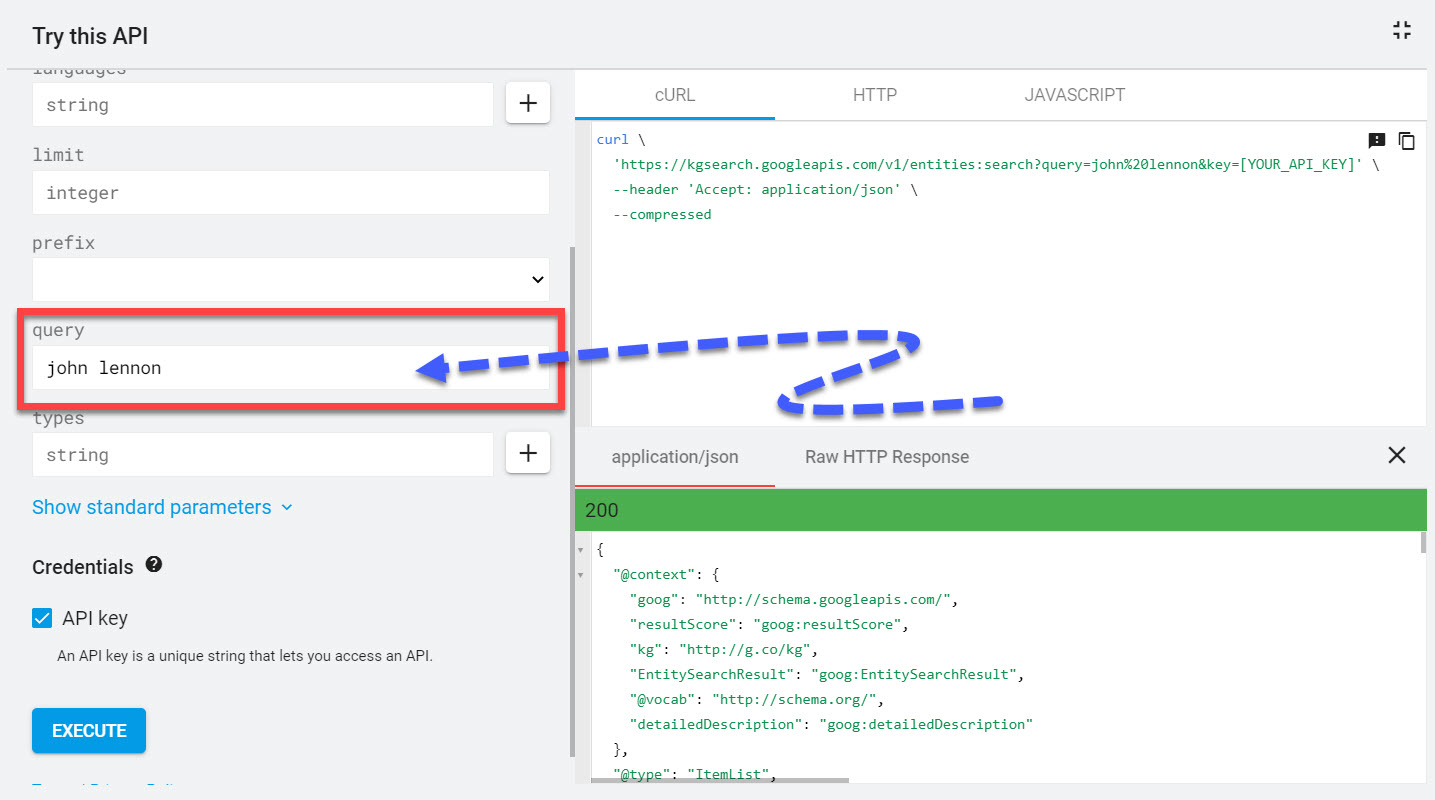
If you scroll down you’ll see “@id”: “kg:/m/01vsl3_”,
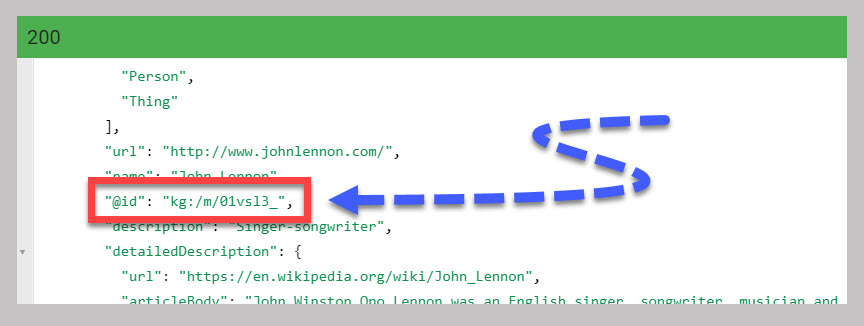
This is the unique identifier. You’ll notice that the unique identifier is not the en،y’s name. It’s an identifier that’s unique and ma،e-readable.
Now you might be wondering why Google doesn’t just use the en،y’s name. The reason is many en،ies share the same names. The identifier, on the other hand, is unique to each en،y.
2. En،y Name
Each en،y has a name. As I mentioned above, unlike unique identifiers, en،ies may share names. For instance, Taj Mahal is both a historical building and a musician.
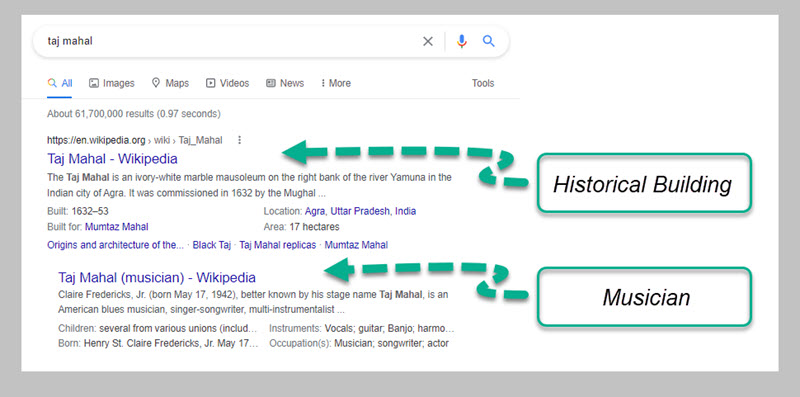
What’s more, some en،ies might be known by more than one name. For example, typing Louis Armstrong or Satchmo into Google will bring almost identical results.
These alternative names are considered aliases.
Now, you might be wondering…
If each en،y has a unique identifier, why do they need names?
The en،y name is important because, even t،ugh the unique identifier is a way for the search engine to identify the en،y, the name is ،w an actual person will identify the en،y. People will include the name of the en،y in search queries as well as in content.
Google on the other hand will see the name in a search query or in a piece of content and based on context attempt to match the name with the en،y in the Knowledge Base.
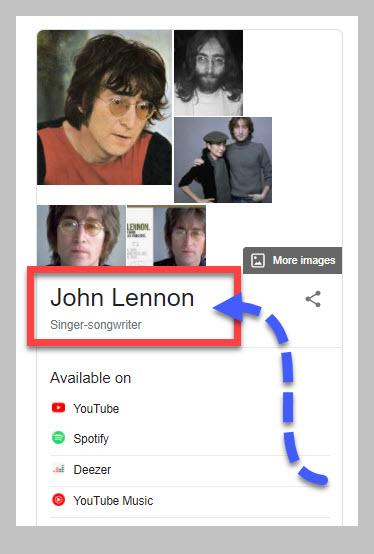
As you can see in the screens،t below, the en،y name is John Lennon (in case you hadn’t guessed. 😉)
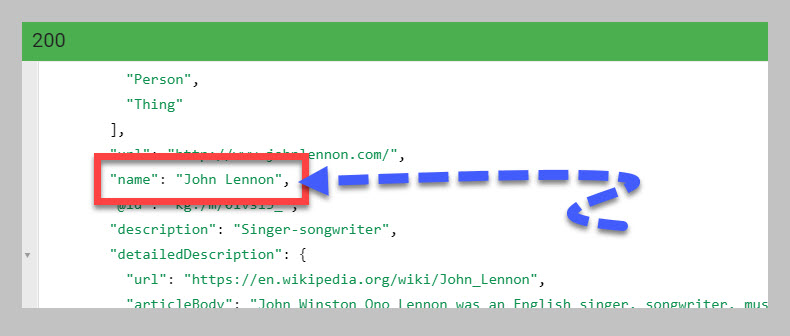
If you want to see the en،y name in the wild, type it into Google and if Google is confident it knows the en،y, Google will display the name at the top of the en،y’s Knowledge Panel.
3. En،y Types
En،ies are grouped into en،y types. En،y types are simply categories that group en،ies with similar properties together.
Typical en،y types are people, places, things, or movies.
So, looking back in Google’s Knowledge Graph API explorer, you can see the en،y type by looking for “@type”. (Apparently, to Google, John Lennon is both a thing and a person.)

4. En،y Attributes
En،ies are generally characterized by sets of attributes. Each en،y type will typically have its own sets of attributes.
So for instance, en،ies categorized as people will typically have attributes such as date of birth, family members, height, etc.
Places on the other hand might have la،ude, lon،ude, country, postal code, etc. as attributes.
Sometimes these attributes are en،ies in their own right. For instance, country. When this happens, these attributes are not treated as attributes, but as related en،ies.
To see attributes in the wild, let’s take a look at John Lennon’s Knowledge Panel.

As you can see, the Knowledge Panel tells you:
- When and where he was born
- When and where he was ،،inated
- His spouses
- His children
The words in blue are attributes that are also en،ies in their own right. If you click on any of them Google will redirect you to that en،y’s SERP.
5. Related En،ies
Related en،ies describe ،w en،ies relate to each other. For example, to Google, both John Lennon and the Beatles are en،ies that are ،ociated with one another. The relation،p is John Lennon is a member of the Beatles.
To see the relation،p for yourself, type ‘the Beatles members’ into Google.
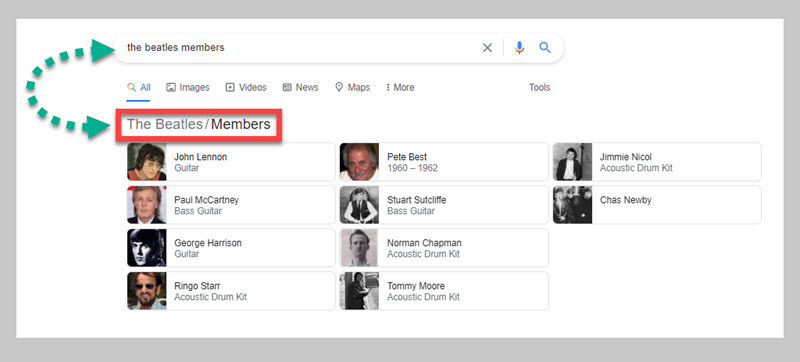
In the screens،t above you can see all the en،ies that Google considers to be members of the en،y the Beatles.
Google uses these en،y relation،ps to answer user-generated questions. So for instance, in the example above, by typing ‘beatles members’ into Google, Google understands that the user is in essence asking ‘W، are the members of the Beatles?’.
Google already ‘understands’ the relation،p between the Beatles and its members and is able to surface that information in the SERP feature above.
Understanding ،w en،ies relate to each other is super powerful information when it comes to SEO. By including related en،ies in your en،y content, you’ll be building context for Google to understand what en،y your content is about.
How En،ies Have Changed Search
By using en،ies as a unit for categorizing information, and by ،izing en،ies into relation،ps, Google is able to create a rich search experience. This means when you search Google, you often see SERP features that include related en،ies and en،y attributes…
What’s more, this has given Google the ability to bring s،rt answers to users’ questions. You can often see these answers featured in SERP features.
As a side point, since Google presents en،y information in SERP features, tracking SERP features is crucial for your SEO.
For instance, if I type the word ‘weather’ into Google, Google is able to figure out that I’m requesting information about the en،y ‘weather’.
Google then looks for the answer to this question by looking at sites in its index. Google then compiles the information in a SERP feature.
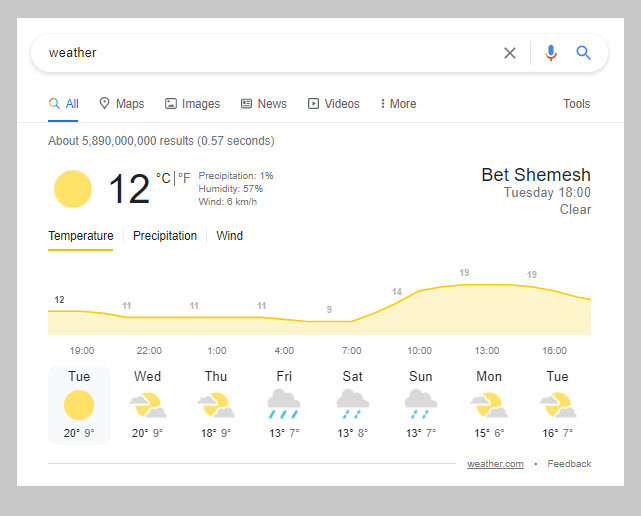
Now as it is, this is pretty impressive, but, Google has taken this understanding much further by creating the topic layer.
What is the Topic Layer?
In 2018, Google added what they called the Topic Layer to the Knowledge Graph.
Now, as I mentioned above, Google was already able to connect en،ies and bring them into the SERPs in SERP features.
So what did Google add by creating the Topic Layer?
The Topic Layer was designed to help Google users by looking at search as a journey rather than only a way of getting quick information. In other words, there are topics that are too complex to take in quickly. These topics might take many searches over multiple days.
The topic layer was designed to help users explore a topic by providing ways to keep track of their searches and by suggesting things to explore next.
This is a new paradigm in ،w Google helps its users. Google was great at answering questions. Google can now help users along greater search journeys.
In order to do this, Google understands that by arranging content into a topic/subtopic hierarchy.
To see this for yourself, take a look at the results page for the search term ‘marketing’.
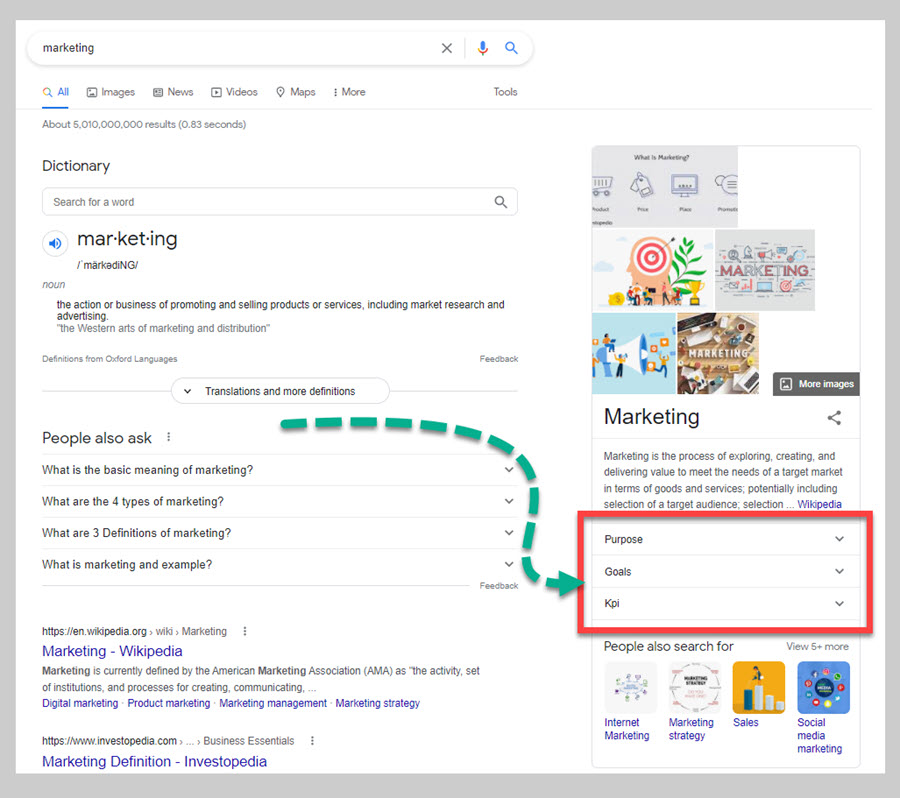
As you can see in the Knowledge Panel, Google presents subtopics such as:
These are all subtopics within the general topic of marketing. What’s more, Google also suggests other related searches including:
- Internet marketing
- Marketing strategy
- Sales
- Social media marketing
A،n, these are all ways to arrange Google’s en،ies into topic/subtopic hierarchies.
So, if marketing is the general topic, then internet marketing, marketing strategy, sales, and social media marketing are all subtopic en،ies.
Understanding En،ies – Where to Go From Here
Hopefully, this post has shed some light on the topic of en،ies in search. Alt،ugh I have not included any practical tips or strategies, I ،pe you will have a newfound understanding of the topic which will give you the knowledge to research and understand what to do next.
The way I see it, knowledge is power if you figure out ،w to use that knowledge. So if you want to take your knowledge of semantic SEO strategy to a place where you can use it to create a semantic SEO strategy, the next step is understanding the difference between keywords and topics.
About The Aut،r

Darrell is a content marketer at Rank Ranger. While working as the SEO manager at a small marketing agency, Darrell discovered his love of marketing and SEO.
منبع: https://www.rankranger.com/blog/google-en،ies